Determination of small amounts of non-volatile residues (µNVR) - practical, fast and economical
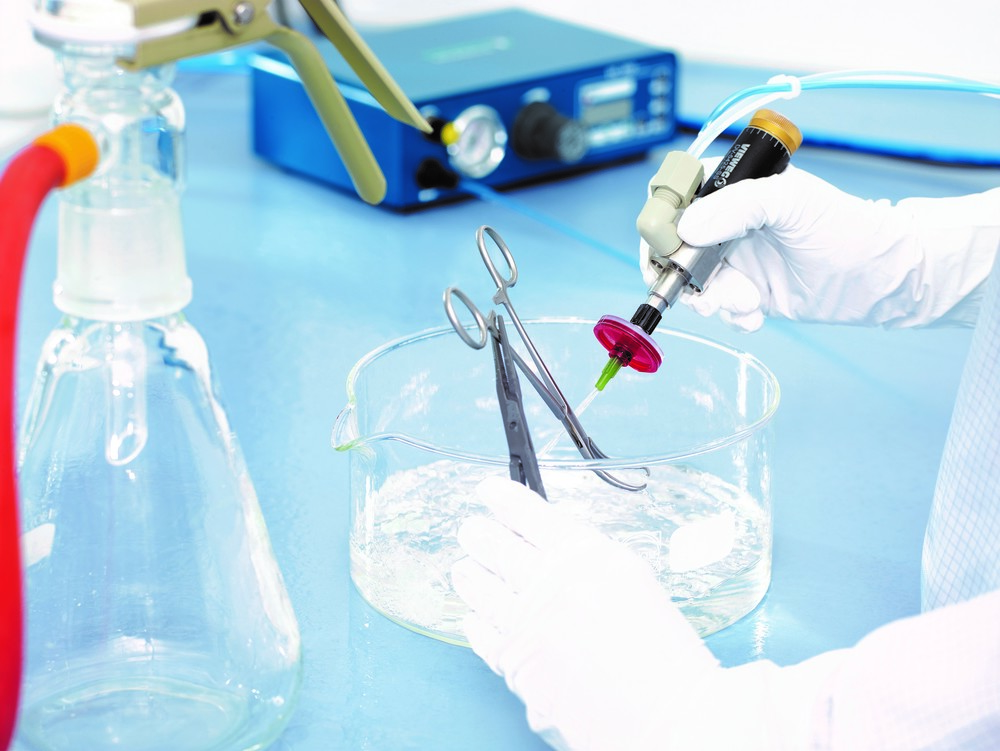
The damaging potential of filmic contamination (oil, grease, fingerprints) is becoming increasingly important in manufacturing processes. The focus here is primarily on organic residues. These contaminants often come from production aids such as oils, greases, anti-corrosion agents, cooling lubricants or cleaning agents. Residues of this type very quickly lead to clear errors in the subsequent manufacturing processes. Such impurities prevent, for example, complete wetting with a layer of paint or significantly reduce the adhesiveness of a contact surface.
The range of measurement techniques known to date ranges from simple methods such as gravimetric determination of residues or contact angle measurement to determine surface tension to IR spectroscopy for characterizing simple organics to complex methods such as coupled gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. This variety of measuring techniques and procedures has not simplified the specification and economic testing of film cleanliness. With the aim of selecting and introducing a uniform and practicable measurement method, the AdhäSa expert group, headed by the Fraunhofer Institute IPA, has developed the new AGREE ® test method.
By participating in this group of experts, CleanControlling has the new test method AGREE ® and can thus carry out fast and economically sensible component tests.
Detailed information on this new test method for filmic component cleanliness can be found here .
To the original article