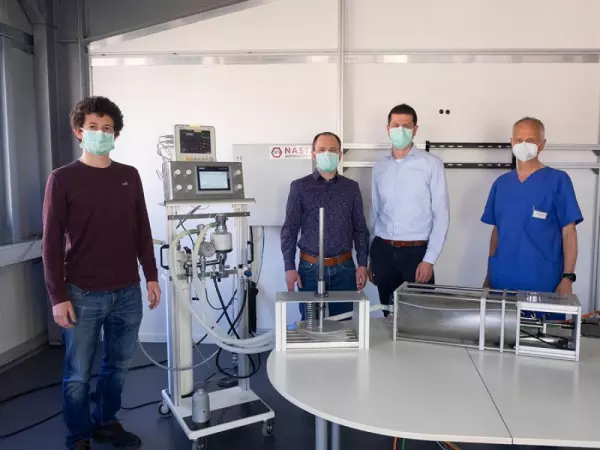

SOGA was a partner in the development of urgently needed ventilators In 2020, the Covid19 crisis...
Portal and digital medical technology fair of the largest MedTech cluster in Germany
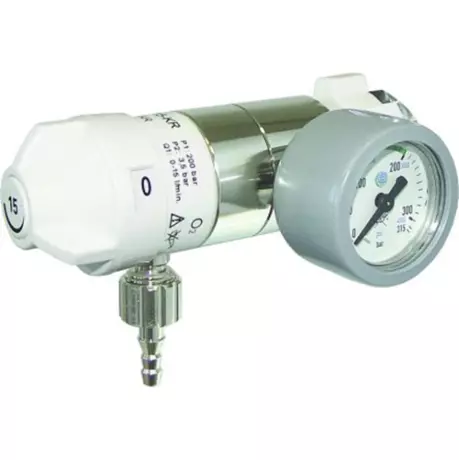

Gas supply - AEROway 0-30 L/min. pressure...
AEROway pressure reducer 0-30 L/min. for oxygen High-pressure manual connection G 3/4″...
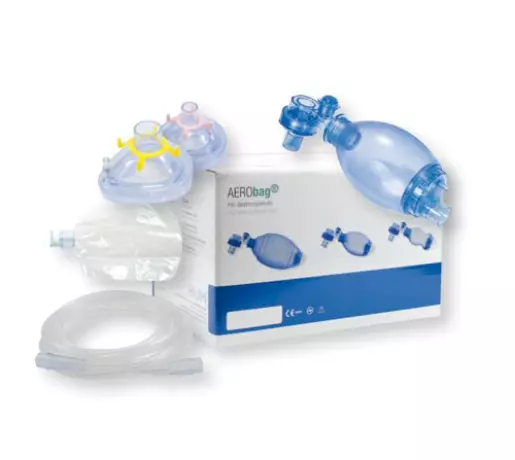
Gas supply - resuscitation bag AEROway resuscitation...
AEROway resuscitator silicone children Resuscitator silicone for children Bag 550ml O2 reservoir 2,6...

The use of ventilators in pulmonary medicine is becoming increasingly common. These devices help to increase oxygen in the air we breathe and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. These fancy pieces of technology are designed to provide oxygen to patients who are unable to breathe on their own. The most common types of ventilators are powered by gas or electricity and are used in intensive care. Read on to learn more about the different kinds of ventilators.
A ventilator is a computerized machine designed to help a patient breathe. Often, it's used to support the respiratory system in a person suffering from a lung or heart failure. These devices are not cheap, and the cost of these machines can be extremely high. But they're vital for patients suffering from various lung diseases. If your loved one needs a ventilator, it's important to get the best one.
In order to use a ventilator safely, you must understand the basic working principle of the device. A computerized ventilator is a complex machine that controls airflow and pressures. When the machine is in use, it can cause a variety of problems. It can be hard to regulate the airway pressure, which can affect the patient's quality of life. If you're a respiratory therapist, this webinar will give you a better understanding of how ventilators work and how they can prevent them from being a source of respiratory disease.
A ventilator is a life-saving machine that helps a patient breathe. It's a medical procedure that requires a team of medical professionals, including a doctor, respiratory therapist, and a nurse. In a pulmonologist's office, you'll see a respiration therapist, a nurse, and a paramedic. They can assist you in managing your patient's life.
A patient's circuit will consist of three durable plastic tubes. These tubes are separated by their function. There are two types of ventilators. Noninvasive methods use a nasal mask and noninvasive methods use a tracheotomy cannula. However, noninvasive methods require a tracheotomy can. The latter method is often more comfortable for the patient. It is essential to use a CPAP machine when the patient's airway is blocked.
A modern ventilator consists of a compressible air reservoir, air and oxygen supplies, and a disposable patient circuit. It can deliver room-air or a mixture of oxygen and air. A turbine delivers the air-oxygen mixture into the patient's lungs. The ventilator can be adjusted to provide the correct pressure for the patient. The exhaled air is released through the manifold. Its elasticity makes it possible to provide a more natural breathing environment.
Ventilators pulmonology may also refer to a physician who specializes in a specific type of respiratory disorder. The respiratory system is closely related to the heart, and a pulmonologist who specializes in pulmonary disease may also be a cardiac specialist. A pulmonologist's specialty often involves critical care, as they treat very sick patients in ICUs. It is a difficult job to make a diagnosis without the right information.
In an emergency, a ventilator can save a life. These devices are complex and difficult to operate. They are also very expensive and require a trained medical professional to use them. As a result, the shortage of ventilators is one of the greatest healthcare issues of our time. Thankfully, there are ways to solve this problem and prevent more lives from being lost. The following are some of the top reasons why people need to use a ventilator.
The first major development of a ventilator was the production of an improved motor. Several manufacturers attempted to improve the performance of their equipment by incorporating a more advanced technology. The East Radcliffe and Beaver ventilators used bicycle hub gears and automotive windscreen wiper motors to power them. However, these electric motors were problematic in operating rooms and posed an explosion hazard to anaesthetics. The solution to this problem came in the form of gas-driven ventilators developed by Roger Manley of the Westminster Hospital in 1952. These were deemed the most successful models in Europe.
The earliest ventilators were powered by a pneumatic system. The AdvaMed member companies began developing new manufacturing lines and repurposing existing ones. The member companies were also implementing new shift lines for production. Many companies also partnered with other industries and third parties to improve their supply chains. Today, gas-powered ventilators are the most popular ventilators, and the U.S. is making an effort to make more ventilators.
The first mechanical ventilators came on the market in the 1970s. These were designed by Oxfordshire-based Penlon and are approved by the UK government. The company is expecting to build hundreds of units of these for UK hospitals next week. By the beginning of May, it is anticipated that the company will be making more than 1,500 ventilators per week. The second mechanical ventilator was built by Smiths, a Luton-based company. It was designed by 100 academics and uses pressurised medical oxygen.
Modern ventilators are controlled by a small embedded system and are very accurate in their adjustments. As a result, they can be fine-tuned to provide steady air exchange. The invasive method, known as tracheotomy cannula, requires a patient to undergo intubation. This method is more comfortable for long-term care. In addition, these mechanical ventilators are easy to use.
The manufacturers of mechanical ventilators plan to increase their production capacity to about 5,000 units per week. Despite the high demand for ventilators, the number of Coronavirus cases in the U.S. has exceeded 190,000, and the number of sick patients is steadily increasing. In response to the increasing need for medical equipment, a few Canadian companies have begun production. These include Bayliss Medical Inc., Thornhill Medical Inc., GE Healthcare, and Canadian Emergency Ventilators.
Another type of mechanical ventilator is the Ambu Bag. This device is compact and lightweight. It also has a programmable function, which allows the patient to control the ventilation rate. Using a ventilator for COVID-19 infection can be dangerous for patients. It is imperative to use the proper ventilator for COVID-19. You should consult a physician before undergoing this treatment. This is a serious medical condition, and mechanical ventilators can be life-saving.
A ventilator can be life-saving if the patient is breathing. A ventilator will drive air into the lungs and release oxygen. In this way, it will keep a person alive and safe. In this case, the patient will experience a lower respiratory rate than normal. Besides, the COVID-19-related infections can be dangerous, and the resulting fluids are poisonous and can even cause death. Fortunately, the COVID-19-related problems are not life-threatening.
A ventilator is an essential medical tool. When a patient is unable to breathe on their own, a ventilator helps them do so. These devices are designed to push air that contains increased oxygen into the lungs. They also help exhale carbon dioxide. This is an important benefit. The respiratory system can be very vulnerable, and a ventilator can be used in the event of a lung injury. It can save a patient's life.
A ventilator is a breathing device that helps a patient breathe. These devices are used in critical illnesses and during surgeries. The ventilator is connected to a patient with a tube that goes through the mouth and down the main airway. A mechanical ventilator will not stop working until the patient is able to breathe on their own. In some cases, a ventilator can cause a heartbeat. These devices have a range of benefits and are often necessary in a hospital.
Become a digital exhibitor yourself in the online portal of the largest and best-known MedTech cluster region in Germany and inform the world of medical technology about your products and services as well as about news, events and career opportunities.
With an attractive online profile, we will help you to present yourself professionally on our portal as well as on Google and on social media.