
Homogeneous light in combination with a constant temperature and humidity is necessary to achieve id...
Portal and digital medical technology fair of the largest MedTech cluster in Germany

Homogeneous light in combination with a constant temperature and humidity is necessary to achieve id...
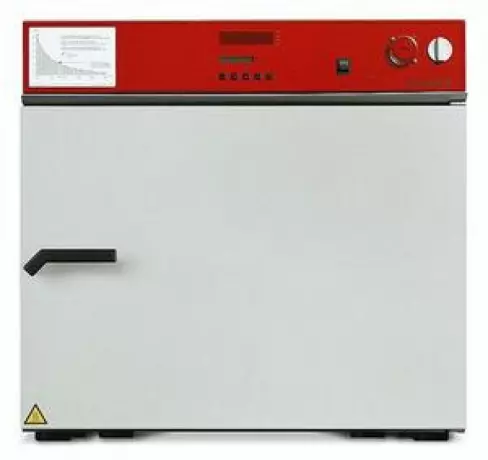

A BINDER heating oven with a silicone- and dust-free inner chamber and a symmetrical air flow provid...
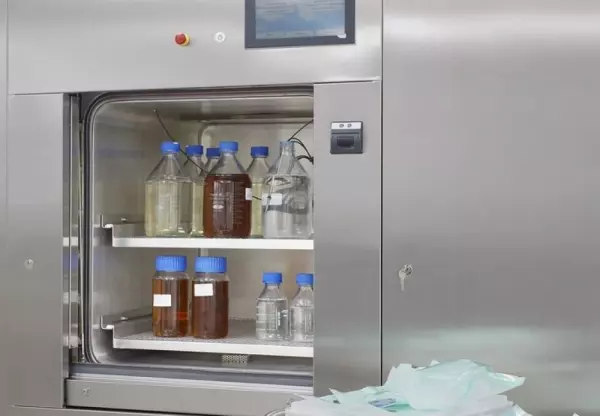

Tests as part of the validation of instructions...
In the same way as with processing of medical devices (cleaning and disinfection) the manufacturer o...
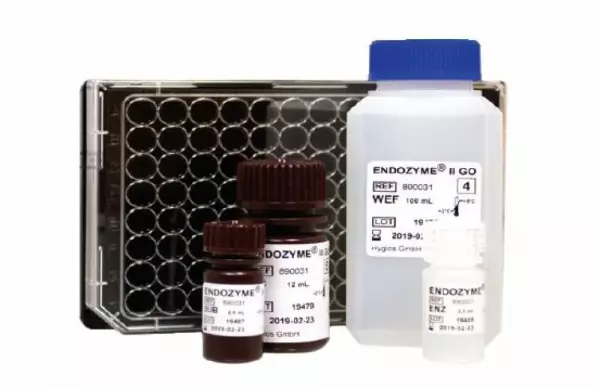
ENDOZYME® II GO (Endotoxin test)
MAIN BENEFITS: Fluorescence end-point assays in 96-well microplate format with methodologie...

BINDER drying chambers: top-quality laboratory...
BINDER laboratory ovens with gravity convection or forced-air convection are renowned for their qual...

BINDER humidity chambers stand out when testing material behaviors under constant temperature and hu...

Ultra low temperature freezers
The spotlight is on environmentally-friendly design in the new BINDER ultra low temperature freezer....

BINDER environmental chambers are perfectly suited to material testing under dynamic conditions. The...
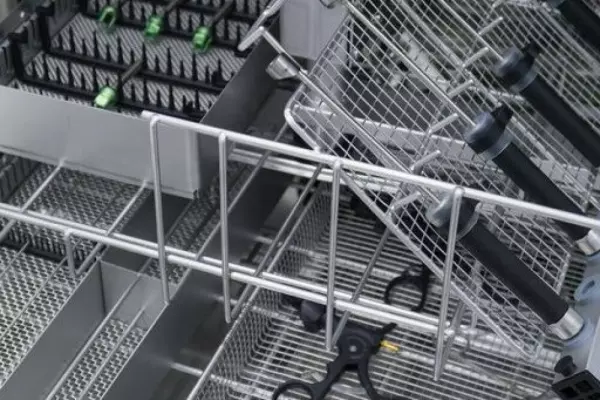

Tests as part of the validation of instructions...
Manufacturers and distributors of medical deviceswhich are designed for reuse, must provide informat...

The completely redesigned Avantgarde.Line incubators with gravity convection or forced convection ar...
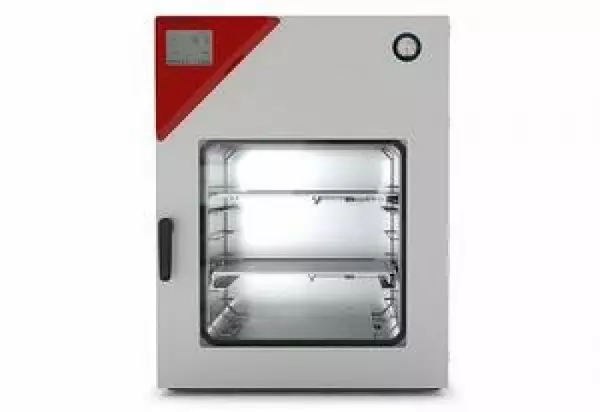

Both BINDER vacuum drying chamber models enable effective drying without residue or damaging the mat...
In-vitro cytotoxicity test (as per DIN EN...
The ability of a substance to damage cells or tissue is referred to as cytotoxicity. The ...
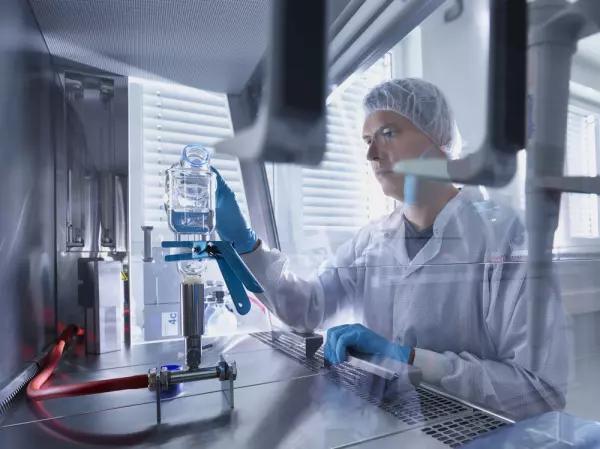

Endotoxin test (as per USP 85 and Ph. Eur....
Endotoxins (ancient Greek endo: "inside", "within", toxins, "the poisonous...
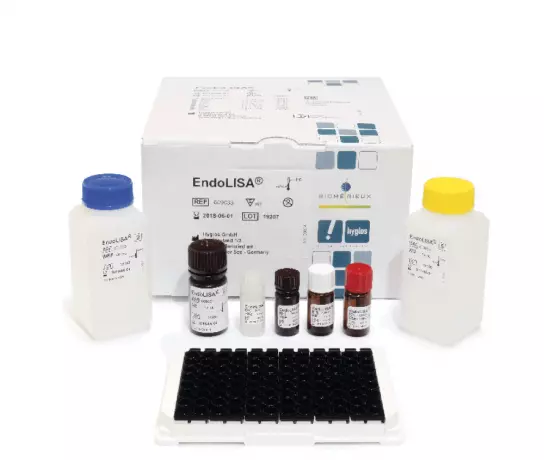
ENDOLISA® (Endotoxin detection)
Overcomes limitations of conventional methods, such as inhibition and enhancement...

ENDONEXT™ Bacterial Endotoxin Testing
The Evolution of Endotoxin Detection happens now! As part of any general pyrogen testing strategy...

BINDER refrigerated incubators are gentle on samples and provide high-quality performance. Every KB...

Determination of bioburden including validation...
The objective of determination of bioburden is to determine the population of viable microorganisms...
Case Study: Arterial Blood Collection Vessels
Whole blood samples are taken from patients using arterial blood collection vessels. The sample is t...

While the philosophical tenets of biomedicine imply that disease, health and wellbeing are intimately related, this does not mean that the two are mutually exclusive. For example, a WHO-type understanding of disease can be balanced with a population-based approach, by pursuing areas of overlap in conceptions of disease and health and investing in infectious disease control strategies. On the other hand, a non-WHO-type understanding of health might ignore the need to evaluate the human-environment relationship.
Although Biomedicine has evolved into a global research enterprise and institution, it has always been critical of the generalist view of science. The idea that disease and health are strictly biological, chemical and physical phenomena is problematic and has spurred much controversy. For this reason, this book outlines several criticisms of the current approach. However, it also demonstrates the importance of keeping an open mind. While this book is not exhaustive, it provides a helpful overview of some of the key arguments supporting a broad-ranging approach to biomedicine.
The history of biomedicine is rich and complex. It relates to physiology and the capacity of humans to resist stress. Among the many sub-disciplines and fields of specialty within biomedicine are: biology, cell biology, embryology, genetics, biotechnology, and gene therapy. Some of the key disciplines and fields of biomedicine include: immunology, genetics, virology, parasitology, and microbiology.
The application of scientific knowledge to medicine and health is an essential goal for biomedical research. This field of study draws from various streams of science and technology. In essence, biomedicine is the intersection of basic science and applied science. It encompasses the fields of biochemistry, microbiology, and clinical and biomedical sciences. The discipline is a multifaceted discipline with many facets. It has the potential to advance the field of medicine and human health.
One of the major areas of biomedicine is regenerative medicine, or the science of replacing cells and tissues. Scientists are working to develop new methods for regenerating cells and organs in the body. They are also studying how to stimulate the body's own repair mechanisms to extend life span. Ultimately, this knowledge is crucial for the improvement of medical care. It's a growing field in biomedicine, and one of the most promising fields is regenerative medicine.
Biomedicine has been a powerful tool in colonial power dynamics. Historically, Western institutions have undermined indigenous medical frameworks and promoted the growth of Western technologies. As a result, low-income and middle-income countries have relied on wealthy Western nations to educate their local biomedical practitioners. Those practitioners often have little incentive to return home and practice their profession. This is a fundamental problem in biomedicine. This is a fundamental area of research in biomedicine.
The study of cellular repair is a major focus of biomedicine. It involves repairing cells and replacing organs. Researchers are developing new techniques to stimulate cellular repair mechanisms in the body. The goal of regenerative medicine is to improve the quality of life for all people. It also involves preventing disease and developing treatments. In this way, the science of biomedicine can make life better for people and society. There are many overlapping fields of biomedicine and it is important to understand the differences between them.
The field of biomedicine is an emerging discipline in medicine. Its development is essential to the future of mankind. Its primary purpose is to improve the health of its people. With improved health, biomedicine helps save lives and reduces the incidence of disease. This is the ultimate goal of biomedicine. Its growth is dependent on human progress, which is the reason why the field of medicine is gaining momentum in society. Its success depends on the success of the innovations.
While biomedicine focuses on disease pathology and treating symptoms after the occurrence of a disease, it is also a vital part of health care. Despite its growing importance in society, the aims of biomedicine differ in every nation. It has been responsible for reducing childhood mortality rates and eradicating major killers. But these achievements have not come without consequences. It has made us more aware of the value of a healthy body.
In contrast to the epistemic priority of biomedicine, the critiques of biomedicine are different in their focus. While most of the alternative frameworks are similar to the biomedical framework, they often highlight different features. In many cases, religious-based prescriptions lead to prohibitions of certain actions and substances. Christian Science practitioners and Jehovah's Witnesses both reject biomedical interventions. Generally, religion is seen as an unscientific obstacle to biomedicine, and a source of pain.
Become a digital exhibitor yourself in the online portal of the largest and best-known MedTech cluster region in Germany and inform the world of medical technology about your products and services as well as about news, events and career opportunities.
With an attractive online profile, we will help you to present yourself professionally on our portal as well as on Google and on social media.