
Point of Care (PoC) analysis for SARS-CoV-2
Point of Care (PoC) analysis If results are to be available promptly so that quick decisions can...
Portal and digital medical technology fair of the largest MedTech cluster in Germany

Point of Care (PoC) analysis for SARS-CoV-2
Point of Care (PoC) analysis If results are to be available promptly so that quick decisions can...
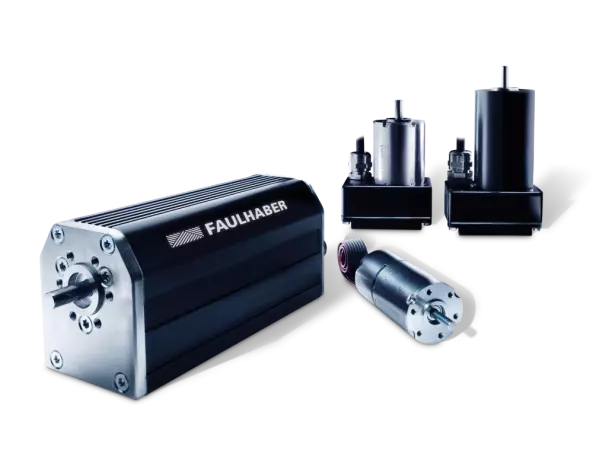

Motors with integrated Electronics
FAULHABER Motion Control Systems combine the high performance of a FAULHABER brushless motor with ta...
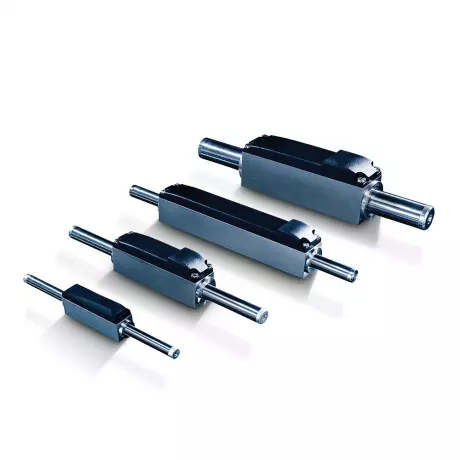

Linear motors from FAULHABER – Exceptionally...
When it comes to executing translational motions as efficiently and flexibly as possible, linear mot...
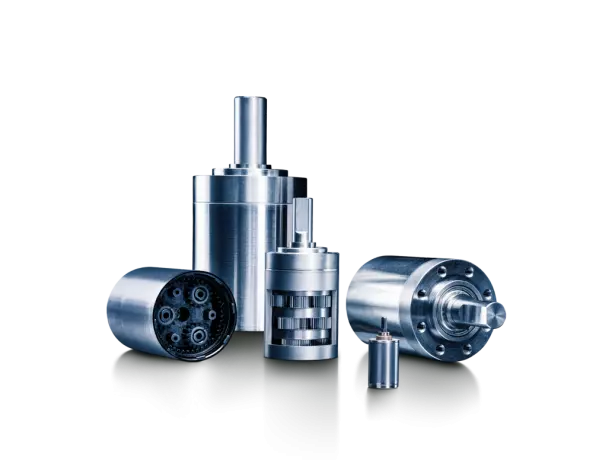

Planetary gearboxes – robust and precise
Thanks to their robust construction, FAULHABER metal planetary gearboxes in combination with FAULHAB...
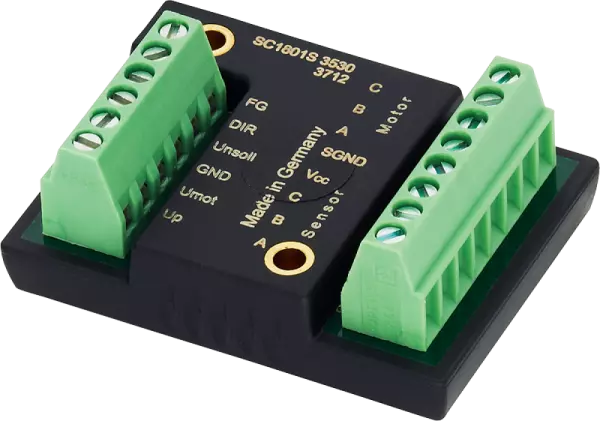
Speed Controllers for speed control
FAULHABER Speed Controllers are specifically designed to get the most out of FAULHABER DC and BL mot...
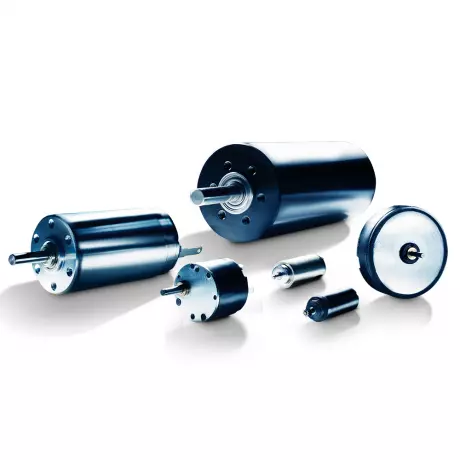

Coreless DC motors from FAULHABER – without...
Coreless DC motors from FAULHABER differ from conventional DC motors with iron armatures primarily d...

DC motors with ironless copper coil in skew winding for medical technology, DC motors with cantilever copper coil in skew winding for medical technology, DC motors with copper coil for medical technology, DC motors with copper coil for laboratory technology, DC motors with copper coil for analysis devices, DC motors with copper coil for dental technology, DC motors with copper coil for medical devices, DC motors with copper coil for laboratory equipment, DC motors with copper coil for dental equipment, DC motors with copper coil for medical equipment
The commutator, or switch, is the essential component of a DC motor. It switches the electrical current from an alternating current (AC) to a direct current (DC). This is necessary because the voltage generated in the armature is alternating and therefore the windings of the coils need to be oriented to make the torque act in the same direction. The commutator controls the electromagnetic fields in the coils. Electricity should flow away from the coil and towards it.
When a motor is turned on, the current in the coil starts flowing. The copper wire in the coil is now an electromagnet, and the current is directed anticlockwise through the top part of the coil. This makes the pole of the coil on the left side of the coil the north pole, which attracts the opposite pole. Conversely, the magnetic field on the right side of the coil attracts the opposite pole.
The wire gauge has an impact on the design of a DC motor. The total diameter of the magnet wire has a direct relationship to the potential slot fill, and the actual area of the conductor determines the amount of current flowing through the coil. The larger the gauge, the more copper the coil can hold with less insulation, and it becomes stiffer. This results in a more difficult-to-handle conductor. Smaller gauge wires increase the insulation-to-conductor ratio and allow for more efficient handling.
The commutator, or switch, makes contact with the coil when it is in its upright position. If the current in the coil remained constant, it would stop the motor. To keep the motor working, the commutator breaks contact with the upright coil and moves it toward the other side. The commutator then re-connects the contacts in the opposite direction. The momentum of the coil keeps it going.
The commutator breaks the contact with the upright coil. The current flows through the upright coil and carries it through the opposite torque half cycle. If it were not for the commutator, the motor would not be possible. Asymmetrical motors are impossible to work on DC. If it did, it would be useless. The same is true for the commutator. In both cases, the commutator breaks contact with the upright coil.
The design of the copper coil varies depending on its shape and components. In general, most of the slots in a DC motor are teardrop shaped, while those in the top half of the stator have flat bottoms. Generally, the radii on the top of the stator are smaller than those in the lower half of the coil. However, this does not prevent the windings from spinning at a higher speed.
Become a digital exhibitor yourself in the online portal of the largest and best-known MedTech cluster region in Germany and inform the world of medical technology about your products and services as well as about news, events and career opportunities.
With an attractive online profile, we will help you to present yourself professionally on our portal as well as on Google and on social media.