1 - 9 by 9 results

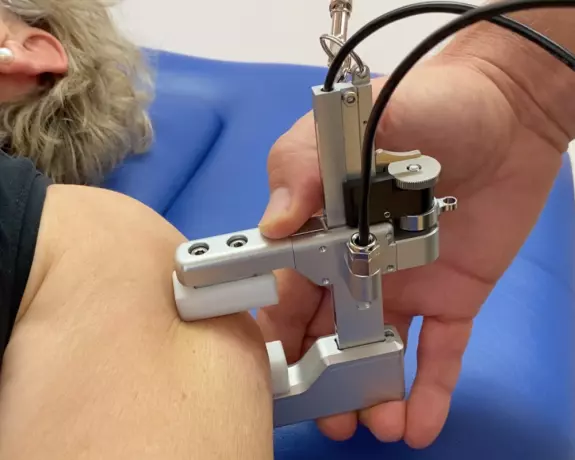
Cibionic® - diagnosis & treatment instrument...
Sustainable therapy results in the shortest possible time - world first Cibionic® With the Ci...

Training seminars & training for therapists...
Academy - train yourself where others go on vacation With advanced training at the Swiss Academy...

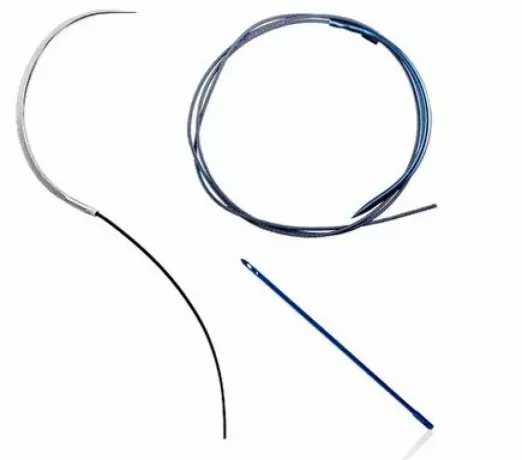
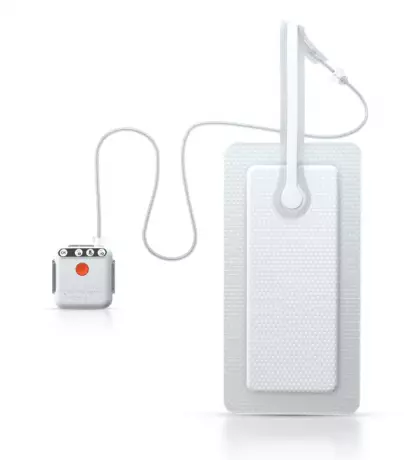
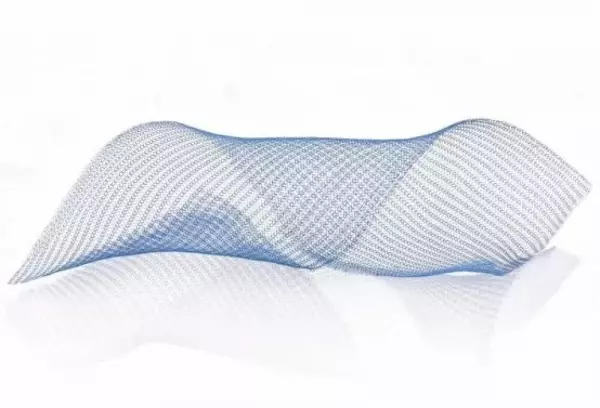
Monopolar and bipolar instruments for HF...
Cutting, coagulation or both in combination has become a standard operating procedure over the last...
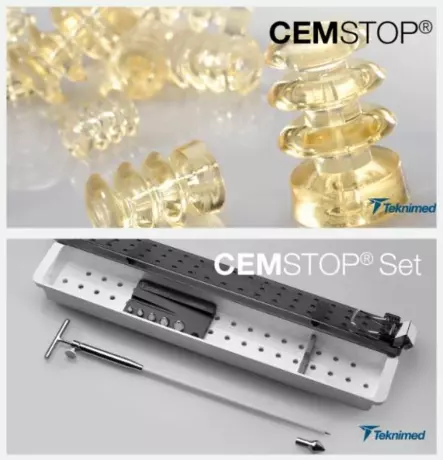

CEMSTOP® Cement plug - biodegradable flexible...
CEMSTOP® Cement plug - biodegradable flexible cement stopper The biodegradable flexible diaph...
1 - 9 by 9 results
Wound Treatment
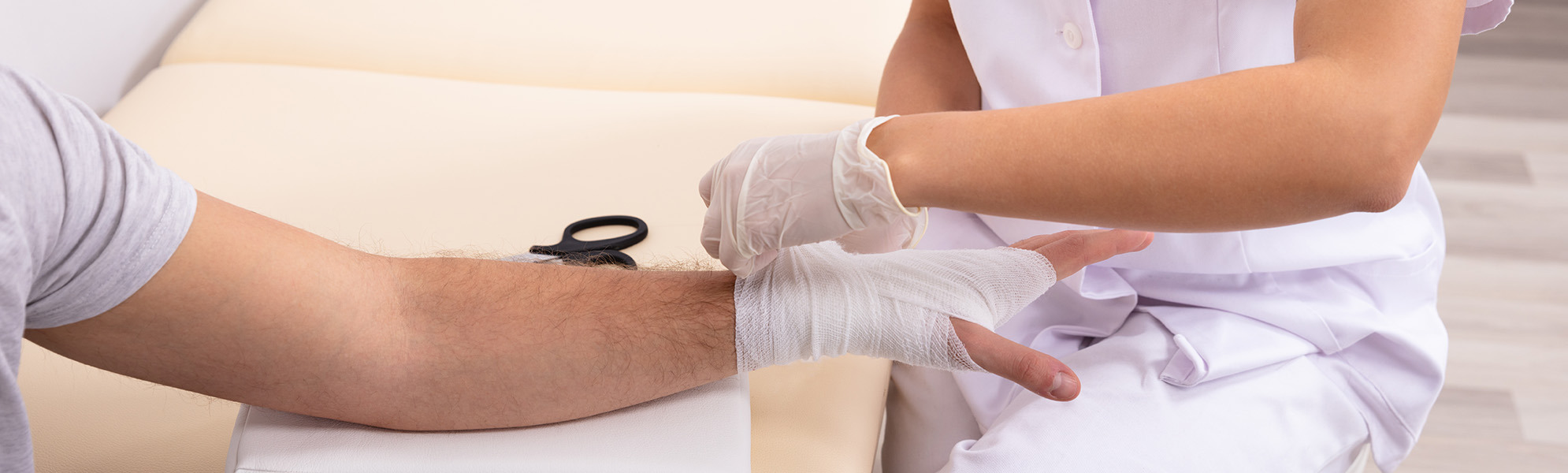
Wound care describes a medical practice that treats wounds in the body. Temporary or temporary wound care is part of first aid. Their main goal is to stop bleeding and control the wound process until professional care is available. Treating wounds with moisturizing bandages is called moist or modern wound care. These moist wound dressings promote the natural healing process and reduce the risk of scars.
In addition, the moist wound environment ensures that the risk of infection is significantly reduced. Moist wound treatment can prevent the formation of crusts, known as char. As a result, newly formed tissue cells do not have to overcome unnecessary obstacles and can migrate and grow better. Dry or traditional wound care is the use of plasters or bandages for treatment without moisturizing substances. In contrast to moist wound healing, a crust forms with dry wound healing. This usually interferes with the natural wound healing process and promotes scarring. For this reason, doctors nowadays increasingly recommend moisturizing wound care.
Wound management is more than just wound care. In fact, wound care is only part of wound management. The spectrum ranges from amnestics to wound records and belongs to experts (so-called wound managers or wound specialists). These specialists are usually specially trained nurses who are familiar with the details of wound types, healing, treatment, pain management, etc. They know how to care for certain wounds. As a rule, wound specialists also work directly with nursing services. Wound care includes measures such as cleaning, closing and caring for open skin injuries.
If the wound is closed within six to eight hours of the injury, this is considered primary wound care. It may have cut a deep wound in the skin and may need to be stitched or closed with sutures. You can also use sticky patches, tissue glue, or classic patch therapy. In the case of targeted wound care, it is important to carefully check the affected skin area beforehand. Superficial wounds, such as abrasions, can usually be treated at home. Wounds that look superficial but are bleeding profusely or are open should be presented to the general practitioner or pediatrician. The first step is to carefully assess the wound here. This involves determining the flow of blood and the depth of the injury. Then the wound began to clean.



















