
Repair service provider for your endoscopy...
endorepair – your partner for the repair of your endoscopy devices and ultrasound probes Ve...
Portal and digital medical technology fair of the largest MedTech cluster in Germany

Repair service provider for your endoscopy...
endorepair – your partner for the repair of your endoscopy devices and ultrasound probes Ve...
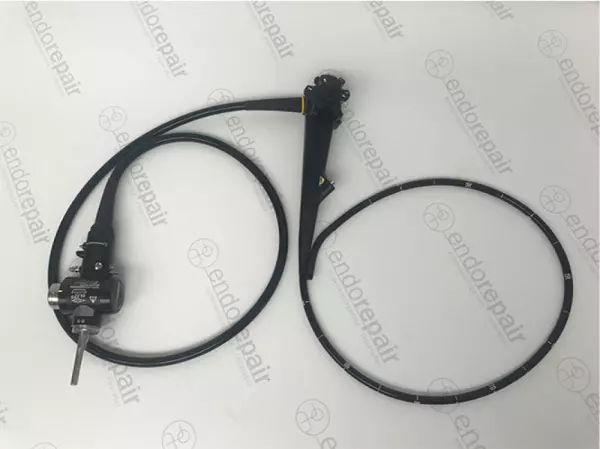

High quality, medical, flexible Gastroscopes...
Our product range of medical endoscopes - High quality, medical, flexible Gastroscopes for expe...

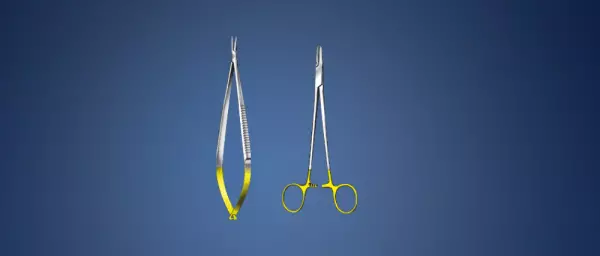
Laparoscopic - High class instruments for...
Innovative concepts implemented in a technically perfect way: for laparoscopy, DUFNER provides two t...

Modular System for Ergonomic and Efficient Work. ErgoSys is an optimal modular system for every f...
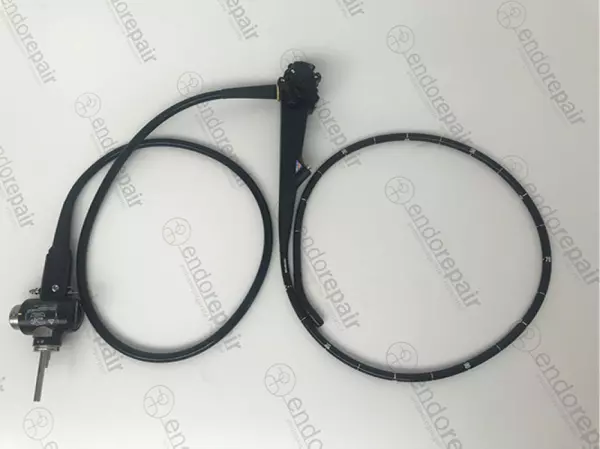

High quality, medical, flexible duodenoscopes...
Our product range of medical endoscopes - High quality, medical, flexible duodenoscopes for exp...
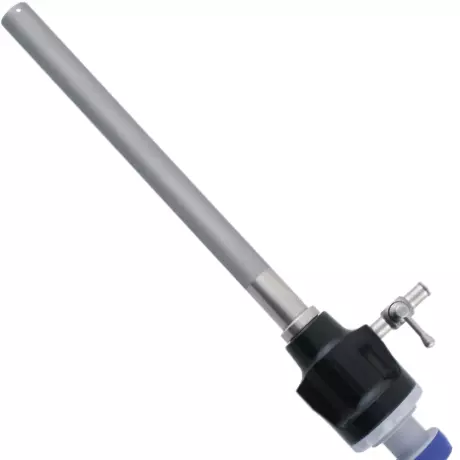

Devices and instruments for laparoscopy by...
Laparoscopy With a complete range of units and instruments for laparoscopy, Tekno-Medical has bec...
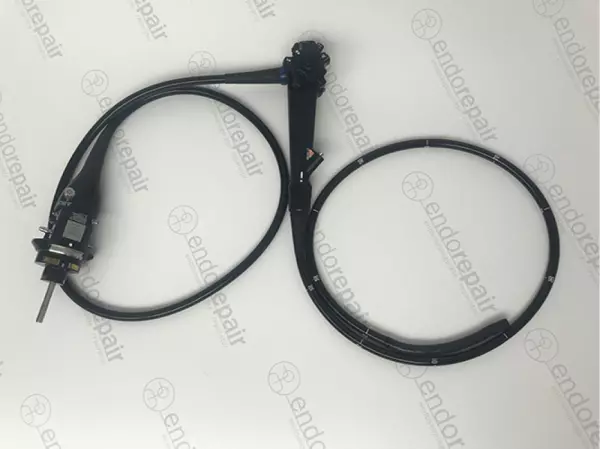

High quality, medical, flexible Coloscopes...
Our product range of medical endoscopes - High quality, medical, flexible Coloscopes for expert...
Instruments and devices for endoscopy
In the field of endoscopy / minimally invasive surgery, ELCON Medical Instruments is able to offer i...
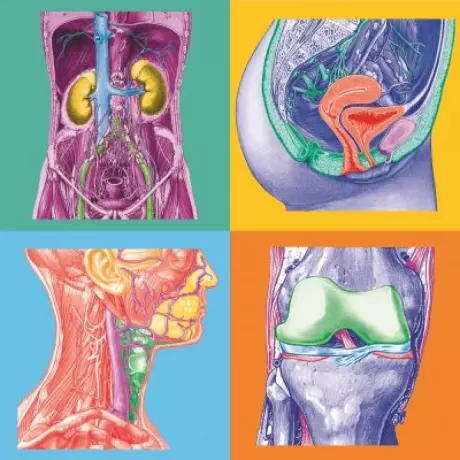
If in the general Surgery, Laryngoscopy, Arthroscopy, plaster (of Paris), ENT surgeon or gynaecology...

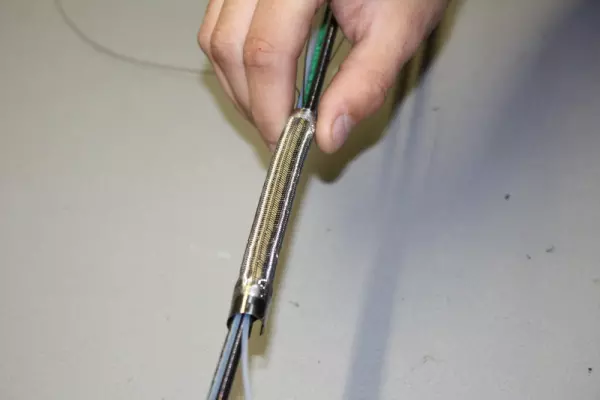
Bypassing repairs and rental equipment for...
At endorepair, we help you minimise your economic downtime. We achieve this on the one hand through...

HSW endoscopes for diagnostics and therapy...
HSW endoscopes for diagnostics and therapy in Laparoscopy Laparoscopes from Henke-Sass, Wol...
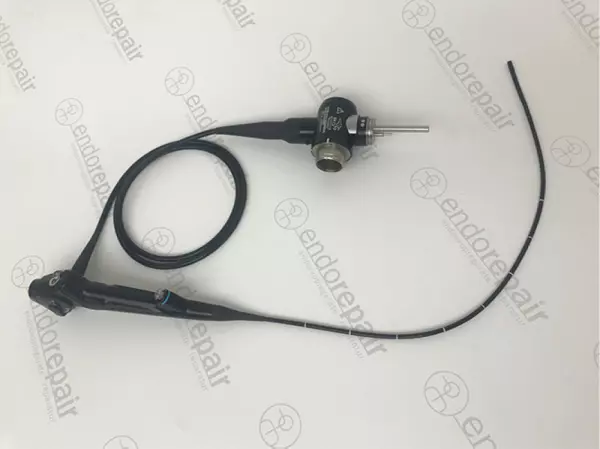
High quality, medical, flexible bronchoscope...
Our product range of medical endoscopes - High quality, medical, flexible bronchoscope for expe...
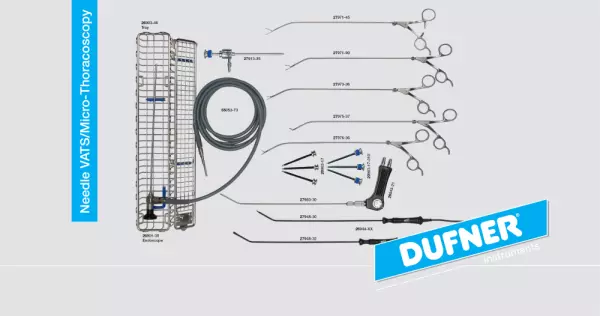
Needle VATS - Mini Thoracoscopy & Laparoscopy
With our new Needle VATS system, new possibilities are open to you. The 3.5mm instruments enable awa...

Endoscopes that can be used in different...
Sinuscopes, otoscopes, arthroscopes, cystoscopes, laparoscopes, hysteroscopes, thoracoscopes, bronch...
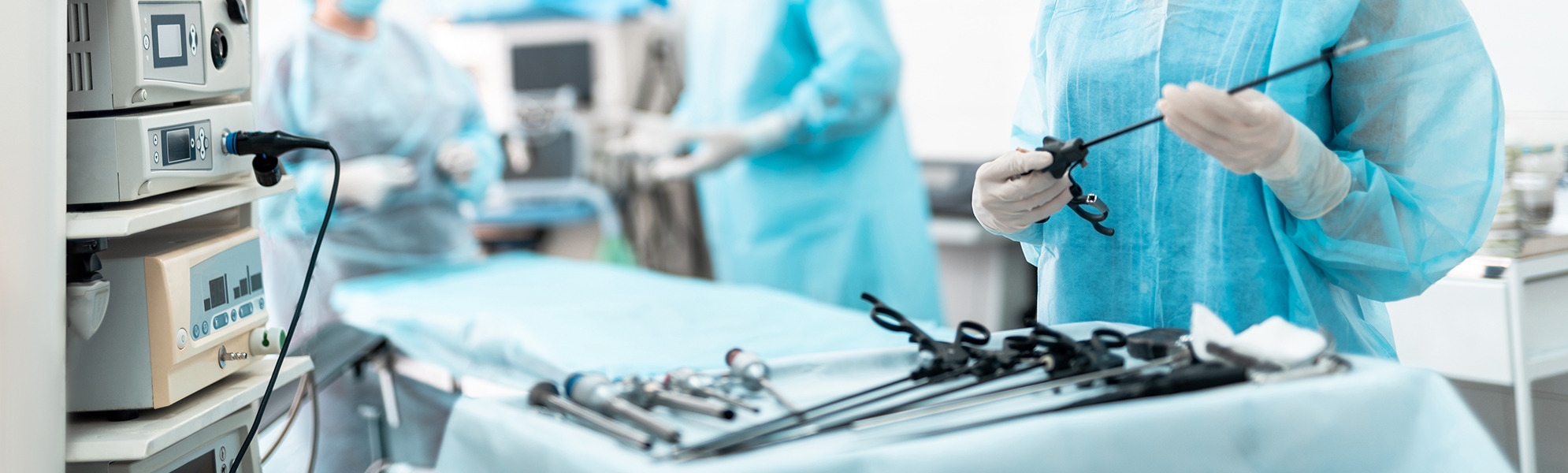
Gynecological laparoscopy is a surgical procedure that avoids incisions in the abdomen when the internal genitals and bladder are disturbed. At the beginning of development, the ovaries were sterilized or a small intervention was carried out. Today, gynecological laparoscopy can be used to perform major tumor interventions that remove lymph nodes along the large vessels, even for cancer of the uterus or cervix. The number of incisions through the abdominal wall is constantly decreasing so that as many instruments as possible can be inserted through the navel (single incision technique). In addition, laparoscopic techniques are becoming more and more complex. This means that very complex and extensive operations can be performed without abdominal incisions, especially in oncology.
The use of robots has not yet found widespread use in gynecology. So far, there have been no advantages over conventional methods, while the costs are considerably higher and the operating time is considerably longer. Laparoscopy (laparoscopy) is a procedure in which the intestines in the abdomen are examined and minor surgical procedures are performed. Compared to open abdominal surgery (open surgery), laparoscopy only requires two to three small incisions (approximately one to two centimeters). This is used to insert laparoscopes and other instruments into the abdominal cavity (keyhole surgery). The main advantage of this so called minimally invasive surgery is that it reduces the burden on the patient. The first human laparoscopy was performed in 1910.
During laparoscopy, the surgeon can view abdominal organs such as the liver, small and large intestines, or internal organs of the genitals on the monitor. If pathological changes (such as inflammation, cancer) are suspected, tissue samples (biopsy) can be taken and then examined under a microscope. In addition, small surgical interventions can be carried out on the organs. After the laparoscopy, the skin incision was sutured and the gas was released again. Depending on the procedure, you can be discharged from the hospital the same day or a few days after the laparoscopy. If other tests (such as ultrasound (x-ray), x-ray) do not give clear results, laparoscopy can be done for diagnostic reasons, e.g. B. to clarify unclear abdominal complaints. In addition, in many cases laparoscopy is a less invasive alternative (body contact) to open abdominal surgery (open surgery). Laparoscopy is not recommended for certain diseases such as coagulopathy, intestinal obstruction, peritonitis, or severe cardiovascular disease. During laparoscopy, the surgeon can determine that open surgery is needed. This is the case, for example, if the result found is greater than the result originally assumed and the keyhole approach cannot be dealt with. Complications (such as profuse bleeding) may also require an abdominal incision.
Become a digital exhibitor yourself in the online portal of the largest and best-known MedTech cluster region in Germany and inform the world of medical technology about your products and services as well as about news, events and career opportunities.
With an attractive online profile, we will help you to present yourself professionally on our portal as well as on Google and on social media.